The Russian language in Ukraine has always been a topic of significant cultural, historical, and political discussion. As Ukraine continues to navigate its national identity, the presence of the Russian language plays a crucial role in shaping its linguistic landscape. This article delves into the complexities surrounding the use of Russian in Ukraine, exploring its historical roots, current status, and future implications.
Understanding the dynamics of the Russian language in Ukraine requires a nuanced perspective. It is not merely about linguistics but also about the socio-political context that surrounds it. The relationship between Ukraine and Russia has been intricate, and language has often been at the forefront of this relationship.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the Russian language's role in Ukraine, offering insights into its historical significance, legal status, and societal impact. By examining various dimensions of this topic, we hope to shed light on the complexities involved and foster a better understanding of the linguistic dynamics in the region.
Read also:P Diddy Past Girlfriends A Comprehensive Look Into His Romantic History
Table of Contents
- The Historical Context of Russian Language in Ukraine
- Legal Status and Linguistic Policies
- Demographics and Regional Variations
- Cultural Impact of Russian Language
- Russian Language in Education
- Russian Language in Media
- Political Implications
- Controversies Surrounding Russian Language
- Future of Russian Language in Ukraine
- Conclusion and Call to Action
The Historical Context of Russian Language in Ukraine
Ukraine's historical relationship with Russia dates back centuries, influencing the linguistic landscape significantly. During the Soviet era, Russian was promoted as the dominant language, overshadowing Ukrainian in many aspects of public life. This policy led to widespread adoption of Russian, especially in urban areas and industrial centers.
Post-independence, Ukraine has made efforts to promote the Ukrainian language, but the legacy of Soviet policies remains evident. Many older generations in Ukraine are more comfortable with Russian, while younger generations increasingly embrace Ukrainian as a symbol of national identity.
Key Historical Milestones
- Soviet Union's language policies emphasizing Russian.
- Ukraine's independence in 1991 and subsequent language reforms.
- Continued influence of Russian in Eastern and Southern Ukraine.
Legal Status and Linguistic Policies
The legal framework surrounding the Russian language in Ukraine has evolved over the years. The Ukrainian constitution designates Ukrainian as the sole state language, but regional laws and amendments have occasionally allowed for the use of Russian in specific contexts.
In 2012, a controversial law granted Russian the status of a regional language in certain areas, sparking debates about linguistic rights and national unity. However, this law was later repealed, reinforcing Ukrainian as the primary language of communication.
Current Legal Framework
- Ukrainian as the sole official language.
- Limited exceptions for Russian in specific regions.
- Ongoing discussions about bilingualism in certain areas.
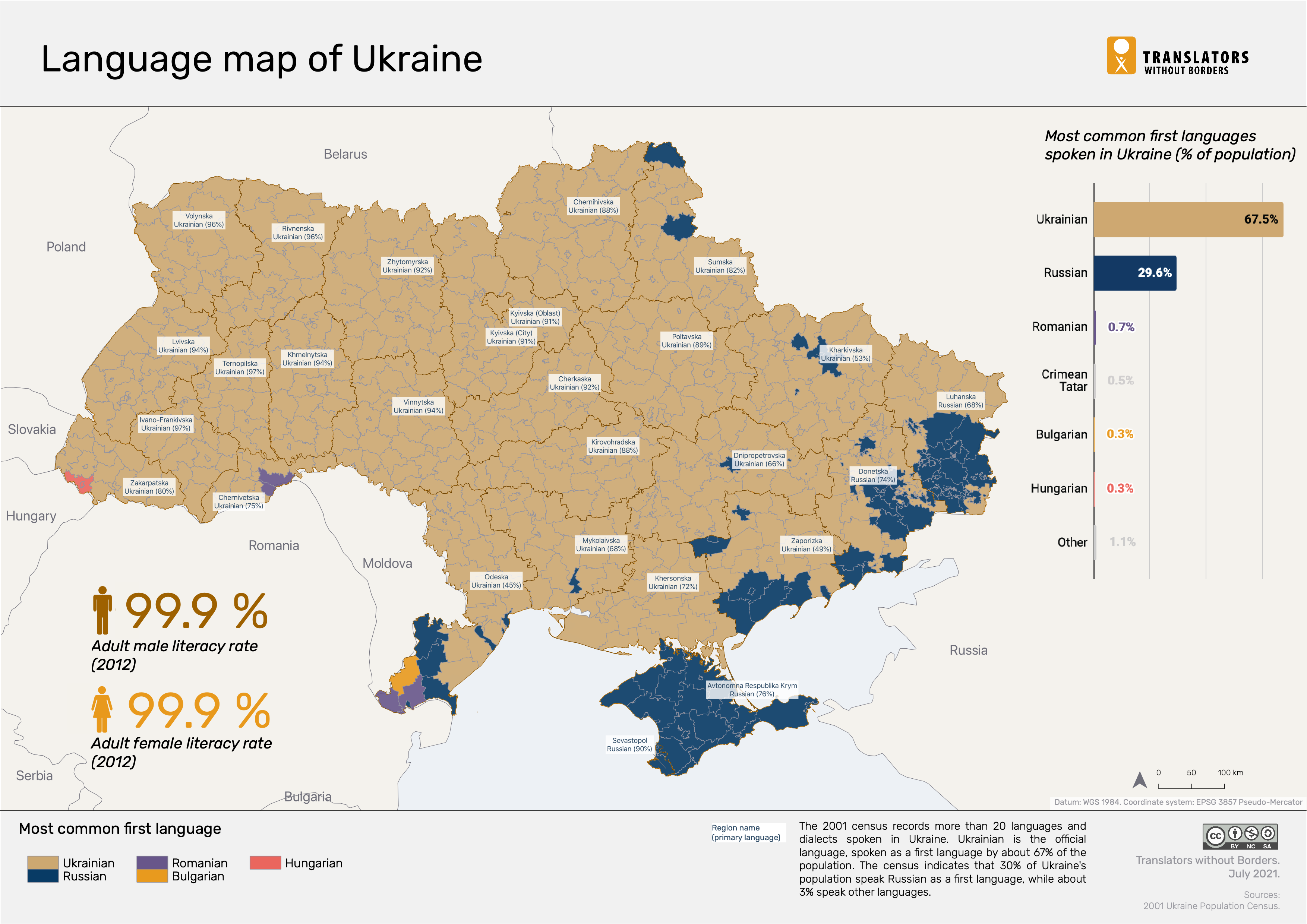
Demographics and Regional Variations
The demographic distribution of Russian speakers in Ukraine varies significantly across regions. Eastern and Southern Ukraine have higher concentrations of Russian speakers, reflecting historical settlement patterns and industrial development.
According to recent estimates, approximately 10-15% of Ukrainians consider Russian their native language, with many more using it as a second language. This regional variation underscores the complexity of linguistic dynamics in the country.
Read also:Donald Trump Polls Analyzing The Political Landscape And Key Insights
Regional Linguistic Patterns
- Eastern Ukraine: Predominantly Russian-speaking.
- Western Ukraine: Strong preference for Ukrainian.
- Central Ukraine: Mixed use of both languages.
Cultural Impact of Russian Language
The Russian language has left a profound cultural imprint on Ukraine, influencing literature, music, and media. Many renowned Ukrainian authors and artists have worked in Russian, contributing to a rich cultural heritage shared by both nations.
However, post-independence Ukraine has seen a resurgence of Ukrainian culture, with efforts to promote Ukrainian-language media, literature, and education. This cultural revival aims to strengthen national identity while respecting linguistic diversity.
Cultural Contributions
- Literary works by Ukrainian authors in Russian.
- Music and film industries with bilingual content.
- Cultural exchanges fostering mutual understanding.
Russian Language in Education
Education plays a critical role in shaping linguistic preferences and proficiency. In Ukraine, the education system has increasingly emphasized Ukrainian as the medium of instruction, but Russian remains an important subject in many schools.
While Ukrainian is the primary language of education, there are still schools and universities where Russian is used, particularly in regions with significant Russian-speaking populations. This dual approach aims to balance linguistic rights with national aspirations.
Education Policies
- Ukrainian as the primary language of instruction.
- Russian language courses offered in schools.
- Higher education institutions with bilingual programs.
Russian Language in Media
Media consumption patterns in Ukraine reflect the linguistic divide, with Russian-language media still holding considerable sway in certain regions. Television, radio, and online platforms offer content in both Ukrainian and Russian, catering to diverse audiences.
Efforts to promote Ukrainian-language media have gained momentum, with government initiatives supporting local content production. However, the popularity of Russian-language media persists, especially among older generations and in Eastern Ukraine.
Media Trends
- Increased production of Ukrainian-language content.
- Continued demand for Russian-language media.
- Emergence of bilingual media outlets.
Political Implications
The role of the Russian language in Ukraine is deeply intertwined with political dynamics. Language policies have often been at the center of political debates, reflecting broader tensions between national identity and regional autonomy.
Political parties and leaders have used language as a rallying point, advocating for either the promotion of Ukrainian or the protection of Russian-speaking rights. This political dimension adds complexity to the linguistic landscape, influencing public opinion and policy decisions.
Political Challenges
- Language as a political issue in elections.
- Regional autonomy and linguistic rights.
- International perspectives on Ukraine's language policies.
Controversies Surrounding Russian Language
The presence of the Russian language in Ukraine has sparked numerous controversies, often tied to historical grievances and geopolitical tensions. Critics argue that promoting Russian undermines Ukrainian sovereignty, while proponents emphasize the need for inclusivity and respect for linguistic diversity.
Recent developments, such as the implementation of language laws and restrictions on Russian-language media, have fueled debates about freedom of expression and cultural rights. These controversies highlight the ongoing struggle to balance national identity with regional sensitivities.
Key Controversies
- Language laws and their enforcement.
- Restrictions on Russian-language media.
- Public reactions and protests.
Future of Russian Language in Ukraine
Looking ahead, the future of the Russian language in Ukraine depends on various factors, including demographic trends, political developments, and cultural shifts. While Ukrainian continues to gain prominence as a symbol of national identity, Russian is likely to remain an important part of the linguistic landscape, especially in regions with significant Russian-speaking populations.
Efforts to promote bilingualism and cultural exchange may help bridge divides, fostering mutual respect and understanding. The challenge lies in striking a balance between linguistic rights and national aspirations, ensuring that all citizens feel included and valued.
Possible Scenarios
- Increased promotion of Ukrainian as the dominant language.
- Persistence of Russian in certain regions and contexts.
- Emergence of bilingualism as a practical solution.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, the Russian language in Ukraine represents a complex interplay of history, politics, and culture. While Ukrainian continues to gain prominence as the national language, Russian remains an integral part of the country's linguistic heritage. Understanding this dynamic requires recognizing the diverse perspectives and experiences that shape it.
We invite readers to engage in this conversation by sharing their thoughts and insights. Leave a comment below or explore other articles on our site to deepen your understanding of Ukraine's linguistic and cultural landscape. Together, we can foster a more inclusive and informed dialogue about the role of language in shaping national identity.