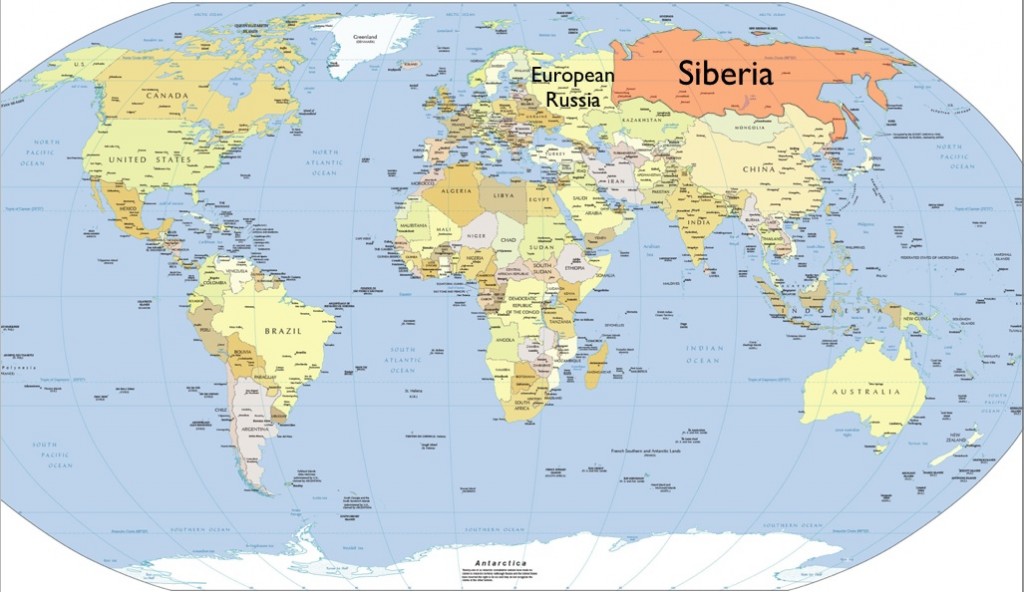
Siberia location is one of the most fascinating and expansive regions in the world. Covering a significant portion of northern Asia, this area has captivated the imagination of explorers, geographers, and scientists for centuries. From its freezing temperatures to its rich biodiversity, Siberia continues to intrigue people around the globe.
Stretching from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east, Siberia location spans over 13 million square kilometers. It represents a significant portion of Russia's total landmass and plays a crucial role in the country's economy, culture, and history. Understanding the geography, climate, and cultural aspects of this region provides valuable insights into its significance on the global stage.
This article delves into the details of Siberia's location, geography, climate, population, and economic activities. By exploring these aspects, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of what makes Siberia such an extraordinary part of the world. Let's dive in and uncover the mysteries of this vast and remote region.
Read also:Donald Trump Haircut The Iconic Style Unveiled
Table of Contents
- Geography of Siberia
- Climate in Siberia
- Population and Demographics
- Economic Activities in Siberia
- Biodiversity and Wildlife
- Historical Background
- Transportation in Siberia
- Tourism Opportunities
- Challenges Faced by Siberia
- Conclusion
Geography of Siberia
Size and Boundaries
Siberia location is immense, covering nearly 13 million square kilometers. It extends from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. This vast area includes a variety of landscapes, from rugged mountains to vast plains, dense forests, and frozen tundra. The southern boundary of Siberia is marked by the Kazakh Steppe and the Mongolian Plateau, while the Arctic Ocean forms its northern boundary.
Key Landmarks
Siberia is home to several notable landmarks that define its geography. Some of these include:
- Lake Baikal: The world's deepest freshwater lake, located in southern Siberia.
- Yenisei River: One of the longest rivers in Asia, flowing through central Siberia.
- Kamchatka Peninsula: Known for its active volcanoes and rugged terrain, located in the far east of Siberia.
Climate in Siberia
Temperature Extremes
The climate in Siberia is characterized by extreme temperature variations. Winters are long and harsh, with temperatures often dropping below -50°C (-58°F) in some regions. Summers, on the other hand, can be relatively warm, with temperatures occasionally reaching up to 30°C (86°F). These fluctuations make Siberia one of the most challenging places to live in the world.
Seasonal Changes
Siberia experiences four distinct seasons, each with its own unique characteristics. Spring and autumn are short, with rapid transitions between winter and summer. The permafrost that covers much of Siberia plays a significant role in shaping the region's climate and landscape.
Population and Demographics
Population Density
Despite its vast size, Siberia's population is relatively sparse. The region is home to approximately 40 million people, with the majority concentrated in urban areas such as Novosibirsk, Omsk, and Krasnoyarsk. The population density is significantly lower than in other parts of Russia, with large areas remaining uninhabited.
Ethnic Diversity
Siberia is a melting pot of ethnicities, with indigenous groups such as the Yakuts, Evenks, and Buryats coexisting alongside Russian settlers. This cultural diversity enriches the region's social fabric and contributes to its unique identity. Efforts are being made to preserve the traditions and languages of these indigenous communities.
Read also:Kim K And P Diddy Video A Comprehensive Look At Their Collaboration
Economic Activities in Siberia
Natural Resources
Siberia location is rich in natural resources, including oil, natural gas, coal, and precious metals. The region's vast reserves of hydrocarbons make it a key player in the global energy market. Additionally, Siberia is known for its timber production, which supports the forestry industry.
Industrial Development
The industrial sector in Siberia is diverse, encompassing mining, manufacturing, and energy production. Cities like Novosibirsk have become hubs for technological innovation, while others focus on heavy industries such as steel production and chemical manufacturing. The region's strategic importance in Russia's economy cannot be overstated.
Biodiversity and Wildlife
Flora and Fauna
Siberia's diverse ecosystems support a wide range of plant and animal species. The taiga, or boreal forest, is home to coniferous trees such as pine, spruce, and fir. Wildlife in Siberia includes iconic species like the Siberian tiger, brown bear, and reindeer. Conservation efforts are ongoing to protect these endangered species and their habitats.
Conservation Efforts
Environmental organizations and government agencies are working together to preserve Siberia's natural beauty and biodiversity. National parks and nature reserves have been established to safeguard the region's ecosystems. These initiatives are crucial for maintaining ecological balance and ensuring the survival of native species.
Historical Background
Early Exploration
The history of Siberia dates back thousands of years, with evidence of human habitation found in archaeological sites across the region. The first Russian explorers arrived in the 16th century, establishing trading posts and settlements. Over time, Siberia became an integral part of the Russian Empire, playing a vital role in its expansion and development.
Modern Era
In the 20th century, Siberia underwent significant changes, including industrialization and urbanization. The construction of the Trans-Siberian Railway in the late 19th century facilitated transportation and trade, connecting the region to the rest of Russia and Europe. Today, Siberia continues to evolve, balancing economic growth with environmental sustainability.
Transportation in Siberia
Trans-Siberian Railway
The Trans-Siberian Railway is one of the most famous transportation routes in the world, spanning over 9,289 kilometers (5,772 miles). It connects Moscow to Vladivostok, passing through major cities and landmarks along the way. This railway remains a vital artery for trade and travel in Siberia, offering both economic and cultural benefits.
Road and Air Networks
In addition to the railway, Siberia has a growing network of roads and airports that connect its cities and towns. While infrastructure development continues to improve, challenges such as harsh weather conditions and vast distances pose obstacles to efficient transportation in the region.
Tourism Opportunities
Adventure Travel
Siberia location offers countless opportunities for adventure travel, from hiking in the Ural Mountains to kayaking down the Yenisei River. The region's untouched wilderness and unique landscapes attract thrill-seekers and nature enthusiasts from around the globe. Tour operators provide guided tours and excursions to ensure a safe and memorable experience.
Cultural Experiences
Visitors to Siberia can immerse themselves in the region's rich cultural heritage by participating in festivals, visiting museums, and interacting with local communities. Learning about the traditions and customs of indigenous peoples provides a deeper understanding of Siberia's history and identity.
Challenges Faced by Siberia
Environmental Concerns
Siberia faces several environmental challenges, including deforestation, pollution, and climate change. The melting of permafrost poses a significant threat to infrastructure and ecosystems, while industrial activities contribute to air and water contamination. Addressing these issues requires coordinated efforts from governments, businesses, and communities.
Economic Disparities
Despite its wealth of natural resources, Siberia experiences economic disparities between urban and rural areas. Many remote communities lack access to basic services such as healthcare and education, highlighting the need for targeted development initiatives. Investments in infrastructure and technology can help bridge these gaps and improve quality of life for all residents.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Siberia location is a remarkable region that offers a wealth of opportunities and challenges. Its vast geography, diverse climate, and rich cultural heritage make it a fascinating subject of study and exploration. From its abundant natural resources to its unique biodiversity, Siberia plays a vital role in both Russia and the global community.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Whether you're planning a trip to Siberia or simply interested in learning more about this incredible region, we encourage you to engage with our content and explore further. Don't forget to check out our other articles for more insights into the world's most fascinating destinations!