Siberia is one of the most fascinating and expansive regions in the world, covering a staggering portion of the Russian Federation. Its vastness and unique geography make it a subject of interest for geographers, historians, and adventurers alike. If you've ever wondered where Siberia is situated, this article will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of its location, geography, climate, and significance.
Siberia has long been shrouded in mystery, often associated with its harsh winters and remote landscapes. However, it is much more than just a frozen wilderness. This region plays a crucial role in Russia's economy, culture, and global influence. Understanding its location is the first step toward appreciating its importance.
From its rich natural resources to its diverse population, Siberia offers a glimpse into the complexities of a region that spans across multiple time zones and ecosystems. Let’s dive into the details and uncover the secrets of this remarkable territory.
Read also:Wake Up In The Morning Feeling Like Fiddy The Ultimate Guide
Table of Contents
- Siberia's Location Overview
- Geographical Boundaries of Siberia
- Climate Conditions in Siberia
- Natural Resources in Siberia
- Population Dynamics in Siberia
- Economy and Infrastructure in Siberia
- History of Siberia
- Cultural Heritage in Siberia
- Environmental Challenges in Siberia
- Travel and Tourism in Siberia
- Conclusion
Siberia's Location Overview
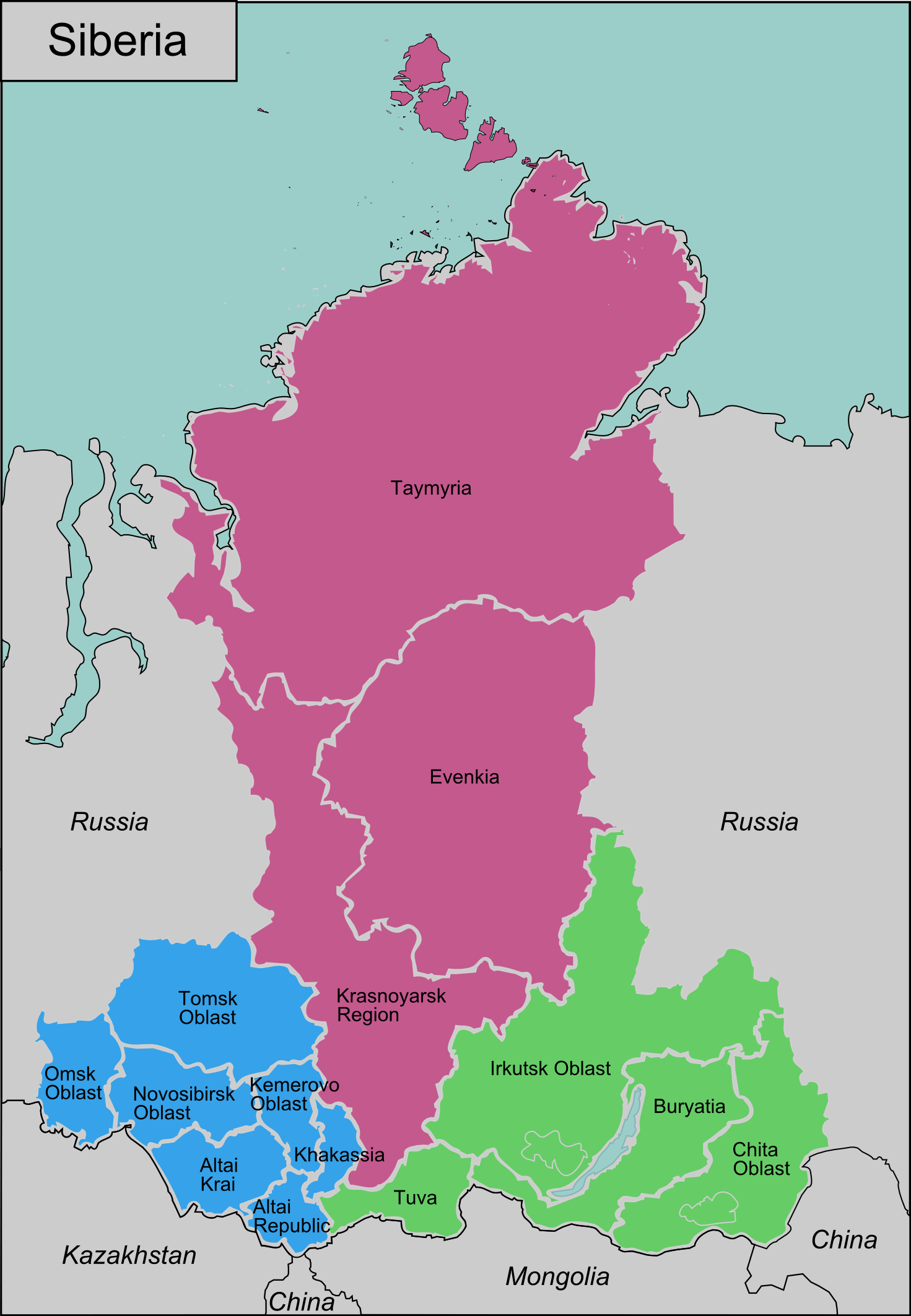
Siberia is situated in the northern part of the Eurasian continent, primarily within the borders of the Russian Federation. It stretches from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east, covering approximately 13.1 million square kilometers. This vast territory accounts for about 77% of Russia's total land area.
The region is divided into three main zones: Western Siberia, Central Siberia, and Eastern Siberia. Each zone has its own distinct geographical and climatic features, contributing to the diversity of Siberia's landscape. The region's location makes it a vital link between Europe and Asia, influencing global trade and politics.
Where Exactly is Siberia Located?
Siberia's exact location can be defined by its boundaries. To the west, it is bordered by the Ural Mountains, which separate it from European Russia. To the east, it extends to the Pacific Ocean, including the Kamchatka Peninsula and the Kuril Islands. In the north, it reaches the Arctic Ocean, while in the south, it borders Kazakhstan, Mongolia, and China.
Geographical Boundaries of Siberia
Siberia's geographical boundaries are vast and diverse, encompassing a wide range of terrains and ecosystems. From the frozen tundra in the north to the dense forests and mountain ranges in the south, Siberia offers a unique blend of natural landscapes.
Key Geographical Features
- Tundra: Found in the northernmost parts of Siberia, the tundra is characterized by permafrost and sparse vegetation.
- Taiga: Covering much of central Siberia, the taiga is the world's largest terrestrial biome, dominated by coniferous forests.
- Mountains: The Sayan, Altai, and Verkhoyansk mountain ranges add to the region's rugged beauty and provide natural barriers.
- Rivers: Major rivers like the Ob, Yenisei, and Lena flow through Siberia, playing a crucial role in its economy and ecology.
Climate Conditions in Siberia
The climate in Siberia varies significantly depending on the region. Generally, it experiences harsh winters with temperatures dropping as low as -60°C (-76°F) in some areas. Summers, on the other hand, can be relatively mild, with temperatures reaching up to 30°C (86°F) in certain parts.
Due to its vastness, Siberia's climate can be categorized into several types, including polar, subarctic, and continental. These variations influence the region's biodiversity and human settlement patterns.
Read also:P Diddys Role In A Raisin In The Sun An Indepth Exploration
Factors Affecting Siberia's Climate
- Latitude: Siberia's high latitude contributes to its long, cold winters.
- Ocean Currents: The Arctic Ocean and Pacific Ocean currents impact the region's weather patterns.
- Topography: Mountain ranges and large bodies of water further shape the local climate conditions.
Natural Resources in Siberia
Siberia is home to an abundance of natural resources, making it a critical region for Russia's economy. It holds significant reserves of oil, natural gas, coal, and precious metals. The region also boasts vast forests and fertile soil, supporting agriculture and forestry industries.
According to a report by the United States Geological Survey (USGS), Siberia contains approximately 25% of the world's known fossil fuel reserves. This wealth of resources has made Siberia a focal point for energy development and international trade.
Key Natural Resources
- Oil and Gas: The Siberian oil fields are among the largest in the world, supplying both domestic and international markets.
- Timber: The taiga forests provide a rich source of timber, supporting the wood processing industry.
- Precious Metals: Siberia is known for its deposits of gold, silver, and platinum, contributing to the global mining sector.
Population Dynamics in Siberia
The population of Siberia is relatively sparse compared to its immense size. As of the latest census, the region has a population of around 38 million people, with the majority living in urban centers such as Novosibirsk, Omsk, and Irkutsk.
Despite its challenging climate, Siberia has been home to various indigenous groups for centuries. Today, it is a melting pot of cultures, with ethnic Russians, Tatars, and numerous indigenous peoples coexisting in the region.
Challenges Facing the Population
- Demographic Decline: Siberia faces challenges related to population decline due to migration and low birth rates.
- Urbanization: Many rural areas are experiencing depopulation as people move to cities for better opportunities.
- Health Issues: The harsh climate and remote locations pose health risks, requiring specialized medical services.
Economy and Infrastructure in Siberia
Siberia's economy is heavily reliant on its natural resources and industrial sectors. The region contributes significantly to Russia's GDP, particularly through its energy exports. Infrastructure development has been a priority, with investments in transportation, communication, and energy networks.
Major infrastructure projects, such as the Trans-Siberian Railway, have facilitated trade and connectivity across the region. These projects continue to evolve, aiming to improve accessibility and economic opportunities for the local population.
Key Economic Sectors
- Energy: Oil, gas, and coal extraction dominate the region's economy.
- Forestry: Timber production and wood processing industries are vital contributors.
- Agriculture: Despite the harsh climate, agriculture plays a role in the regional economy.
History of Siberia
Siberia has a rich and complex history, dating back thousands of years. The region was originally inhabited by various indigenous tribes, who developed unique cultures and traditions. In the 16th century, Russian explorers began venturing into Siberia, gradually expanding their influence over the area.
Throughout its history, Siberia has played a significant role in Russian politics and economics. It served as a place of exile for political dissidents and a source of valuable resources for the empire. Today, Siberia continues to shape Russia's identity and global standing.
Major Historical Events
- Exploration and Colonization: The Russian conquest of Siberia began in the late 16th century.
- Industrial Development: The 19th and 20th centuries saw rapid industrial growth in the region.
- Modern Era: Post-Soviet reforms have transformed Siberia's economy and governance structures.
Cultural Heritage in Siberia
Siberia's cultural heritage is a tapestry woven from the traditions of its indigenous peoples and the influences of Russian settlers. The region is home to vibrant festivals, unique art forms, and a rich oral history that reflects its diverse population.
Efforts are being made to preserve and promote Siberia's cultural heritage, ensuring that future generations can appreciate its significance. Museums, cultural centers, and educational programs play a crucial role in this endeavor.
Indigenous Cultures in Siberia
- Evenks: Known for their reindeer herding and shamanistic practices.
- Yakuts: Celebrated for their horsemanship and traditional crafts.
- Buryats: Influenced by Tibetan Buddhism, they have a rich spiritual tradition.
Environmental Challenges in Siberia
Siberia faces numerous environmental challenges, many of which are exacerbated by climate change. The melting of permafrost, deforestation, and pollution from industrial activities pose significant threats to the region's ecosystems.
Conservation efforts are underway to protect Siberia's unique biodiversity and natural resources. International cooperation and local initiatives aim to address these challenges and promote sustainable development in the region.
Key Environmental Issues
- Permafrost Melting: Leading to infrastructure damage and greenhouse gas release.
- Deforestation: Caused by logging and wildfires, impacting wildlife habitats.
- Pollution: Industrial activities contribute to air and water pollution, affecting human health.
Travel and Tourism in Siberia
Siberia offers a wealth of opportunities for travelers seeking adventure and cultural experiences. From the stunning landscapes of Lake Baikal to the historic cities along the Trans-Siberian Railway, the region has much to offer visitors.
Tourism in Siberia is growing, with efforts to promote eco-tourism and cultural tourism gaining momentum. Travelers can explore the region's natural wonders, learn about its history, and engage with its vibrant communities.
Top Tourist Attractions
- Lake Baikal: The world's deepest and oldest lake, known for its crystal-clear waters.
- Trans-Siberian Railway: A legendary journey across the vast expanse of Siberia.
- Kamchatka Peninsula: Famous for its volcanoes and pristine wilderness.
Conclusion
Siberia is a remarkable region that plays a vital role in Russia's geography, economy, and culture. Its location, spanning across the northern part of the Eurasian continent, makes it a crucial link between Europe and Asia. Understanding where Siberia is situated and its unique characteristics is essential for appreciating its global significance.
We encourage you to explore Siberia further, whether through travel, research, or cultural exchange. Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below, and don't forget to check out our other articles for more insights into this fascinating region. Together, let's uncover the wonders of Siberia!

![[Siberia] All about [Siberia]](https://s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/gmag.io-live-us/games/logos/19046_64648cba0faa7.jpg)
